| cmake | ||
| logger | ||
| test | ||
| .gitignore | ||
| CMakeLists.txt | ||
| CTestConfig.cmake | ||
| Dart.sh | ||
| example.png | ||
| FairLoggerTest.cmake | ||
| Jenkinsfile | ||
| Jenkinsfile.nightly | ||
| LICENSE | ||
| README.md | ||
FairLogger
Lightweight and fast C++ Logging Library
| Branch | Build Status |
|---|---|
master |
|
dev |
Installation
git clone https://github.com/FairRootGroup/FairLogger
mkdir FairLogger_build && cd FairLogger_build
cmake -DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=./FairLogger_install ../FairLogger
cmake --build . --target install
Usage
In your CMakeLists.txt:
find_package(FairLogger)
If FairLogger is not installed in system directories, you can hint the installation location:
set(CMAKE_PREFIX_PATH /path/to/FairLogger/installation ${CMAKE_PREFIX_PATH})
find_package(FairLogger)
find_package(FairLogger) will define an imported target FairLogger::FairLogger.
CMake options
On command line:
-DDISABLE_COLOR=ONdisables coloured console output.-DBUILD_TESTING=OFFdisables building of unit tests.-DUSE_BOOST_PRETTY_FUNCTION=ONenables usage ofBOOST_PRETTY_FUNCTIONmacro.
Documentation
1. General
All log calls go through the provided LOG(severity) macro. Output through this macro is thread-safe. Logging is done to cout, file output and/or custom sinks.
2. Severity
The log severity is controlled via:
fair::Logger::SetConsoleSeverity("<severity level>");
// and/or
fair::Logger::SetFileSeverity("<severity level>");
// and/or
fair::Logger::SetCustomSeverity("<customSinkName>", "<severity level>");
where severity level is one of the following:
"nolog",
"fatal",
"error",
"warn",
"state",
"info",
"debug",
"debug1",
"debug2",
"debug3",
"debug4",
"trace",
Logger will log the chosen severity and all above it (except "nolog", which deactivates logging for that sink completely). Fatal severity is always logged.
3. Verbosity
The log verbosity is controlled via:
fair::Logger::SetVerbosity("<verbosity level>");
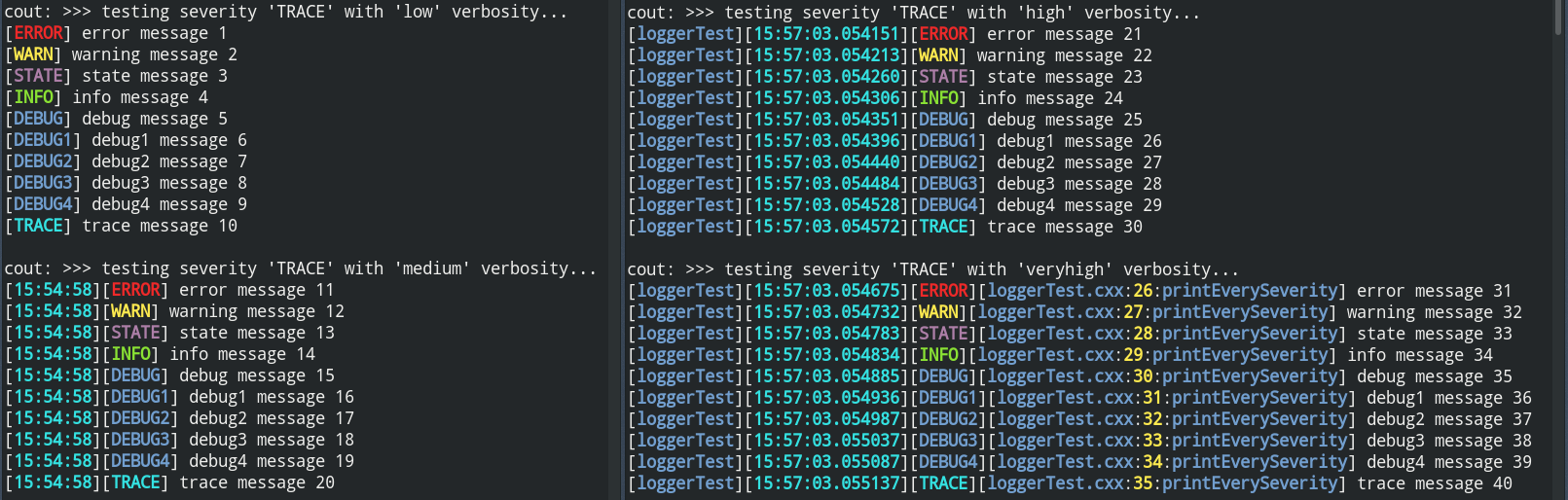
it is same for all sinks, and is one of the following values: verylow, low, medium, high, veryhigh, which translates to following output:
verylow: message
low: [severity] message
medium: [HH:MM:SS][severity] message
high: [process name][HH:MM:SS:µS][severity] message
veryhigh: [process name][HH:MM:SS:µS][severity][file:line:function] message
When running a FairMQ device, the log severity can be simply provided via --verbosity <level> cmd option.
The user may customize the existing verbosities or any of user1, user2, user3, user4 verbosities via:
void fair::Logger::DefineVerbosity(fair::Verbosity, fair::VerbositySpec);
void fair::Logger::DefineVerbosity("<verbosity level>", fair::VerbositySpec);
The fair::Logger::VerbositySpec object can e.g. be created like this:
auto spec = fair::VerbositySpec::Make(VerbositySpec::Info::timestamp_s,
VerbositySpec::Info::process_name);
// results in [HH:MM:SS][process name] message
| Argument | Result |
|---|---|
fair::VerbositySpec::Info::process_name |
[process name] |
fair::VerbositySpec::Info::timestamp_s |
[HH:MM:SS] |
fair::VerbositySpec::Info::timestamp_us |
[HH:MM:SS:µS] |
fair::VerbositySpec::Info::severity |
[severity] |
fair::VerbositySpec::Info::file |
[file] |
fair::VerbositySpec::Info::file_line |
[file:line] |
fair::VerbositySpec::Info::file_line_function |
[file:line:function] |
3.1 BOOST_PRETTY_FUNCTION support
By default, the veryhigh verbosity prints the function name from which the LOG macro was invoked. If you desire a more verbose function signature including the full namespace, return value and function arguments, you can enable support for BOOST_PRETTY_FUNCTION
- globally by compiling FairLogger with the CMake option
-DUSE_BOOST_PRETTY_FUNCTION=ON, or - per translation unit by defining
FAIRLOGGER_USE_BOOST_PRETTY_FUNCTIONbefore including the FairLogger header, e.g.
#define FAIRLOGGER_USE_BOOST_PRETTY_FUNCTION
#include <Logger.h>
In the latter case, the user needs to take care of adding the boost include path to the compiler search path manually (e.g. -I/path/to/boost/include).
4. Color
Colored output on console can be activated with:
Logger::SetConsoleColor(true);
When running a FairMQ device, the log color (console) can be simply provided via --color <true/false> cmd option (default is true).
5. File output
Output to file can be enabled via:
Logger::InitFileSink("<severity level>", "test_log", true);
which will add output to "test_log" filename (if third parameter is true it will add timestamp to the file name) with <severity level> severity.
When running a FairMQ device, the log file can be simply provided via --log-to-file <filename_prefix> cmd option (this will also turn off console output).
5.5 Custom sinks
Custom sinks can be added via Logger::AddCustomSink("sink name", "<severity>", callback) method.
Here is an example adding a custom sink for all severities ("trace" and above). It has access to the log content and meta data. Custom log calls are also thread-safe.
Logger::AddCustomSink("MyCustomSink", "trace", [](const string& content, const LogMetaData& metadata)
{
cout << "content: " << content << endl;
cout << "available metadata: " << endl;
cout << "std::time_t timestamp: " << metadata.timestamp << endl;
cout << "std::chrono::microseconds us: " << metadata.us.count() << endl;
cout << "std::string process_name: " << metadata.process_name << endl;
cout << "std::string file: " << metadata.file << endl;
cout << "std::string line: " << metadata.line << endl;
cout << "std::string func: " << metadata.func << endl;
cout << "std::string severity_name: " << metadata.severity_name << endl;
cout << "fair::Severity severity: " << static_cast<int>(metadata.severity) << endl;
});
If only output from custom sinks is desirable, console/file sinks must be deactivated by setting their severity to "nolog".
License
GNU Lesser General Public Licence (LGPL) version 3, see LICENSE.
Copyright (C) 2017-2018 GSI Helmholtzzentrum fuer Schwerionenforschung GmbH